Synthetic Insulation Production Process: Part 1. Raw Materials
2020-05-20
Understanding of raw materials is essential in the planning phase of garment manufacturing as it allows to find proper materials that best serve to the purpose and maximize the benefits of the selected ones.
In this newsletter and two mores to follow, you will find details about ‘synthetic insulation production process in the order of 1) Production of raw materials, 2) manufacturing, and 3) Production of recycled raw materials, of which demand is increasing recently.
Fibers are classified with filament and stable fiber according to their length. Filament yarns are largely used to produce fabrics and synthetic insulations are made by manufacturing staple fibers. Here, we will focus on staple fiber manufacturing process.
*This production process was explained based on the Melt Spinning process applied to form polyester fibers.
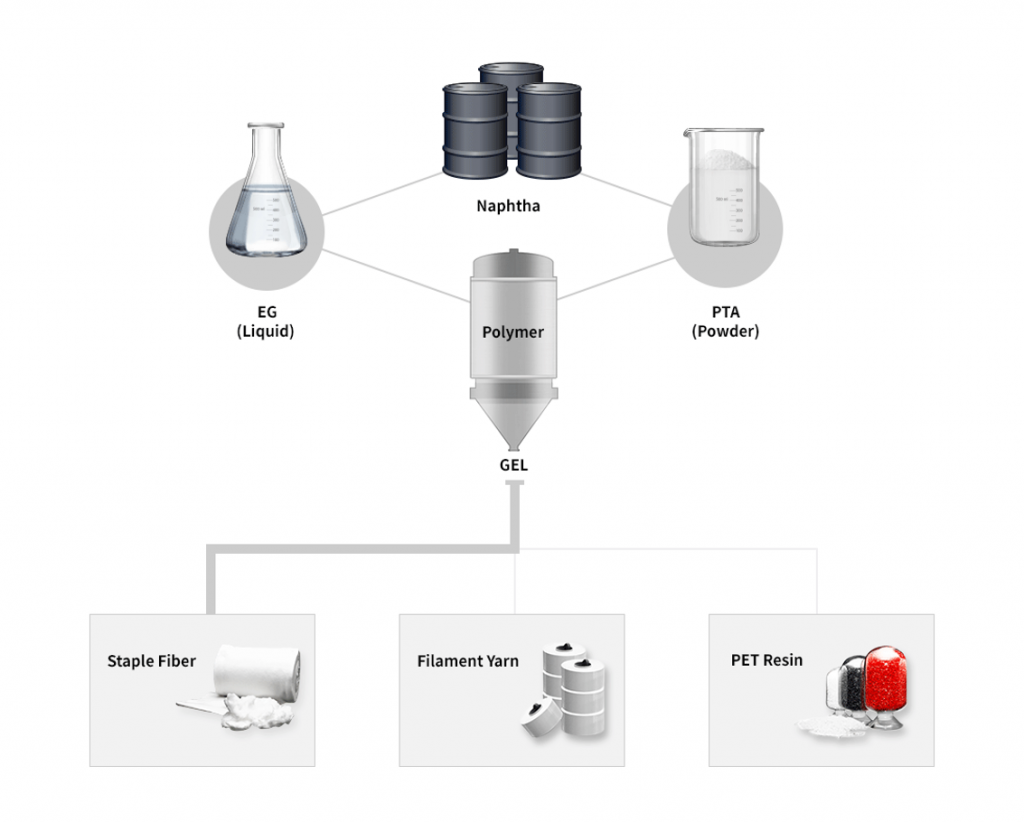
<Staple fiber production process>
Source: Huvis
1. Polymerization
Ethylene Glycol (EG) liquid from crude oil and Purified Terephthalic Acid (PTA, a high purity acid powder) are combined and converted to gel polymer through polymerization performed at a high temperature and pressure. After that, they undergo the spinning process or are produced as chip-type resin fibers.
2. Spinning
The resin is melted by applying heat, and the molten polymer of synthetic is inserted into a vessel and pushed out through fine nozzle holes in spinnerets with pressure to become the polyester staple fibers. Here, the size of nozzle determines the fiber thickness and the finer the holes require more sophisticated technologies.

<Spinneret (left) and spinning nozzles (right)>
3. Drawing
The polyester fibers are pulled through rollers to make them longer and undergo the texturing process by which synthetic fibers are modified to change their texture or physical appearance. Such texturizing techniques include bulking where the fibers are strongly twisted and untwisted to have a waviness or crimp. Drawing is a critical process as it determines the product quality.
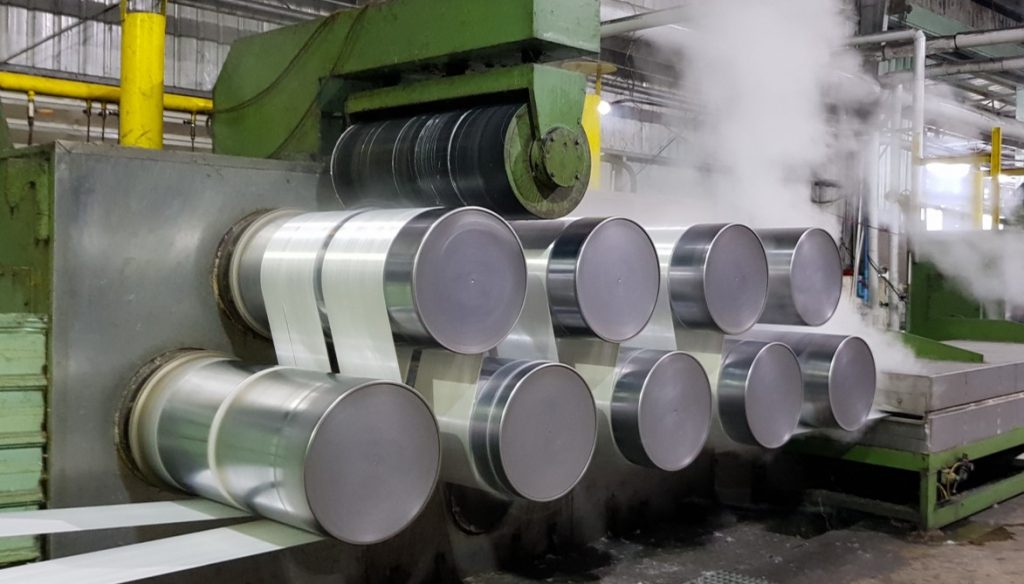

<Drawing process>

<Polyester fibers after texturing>
4. Cutting
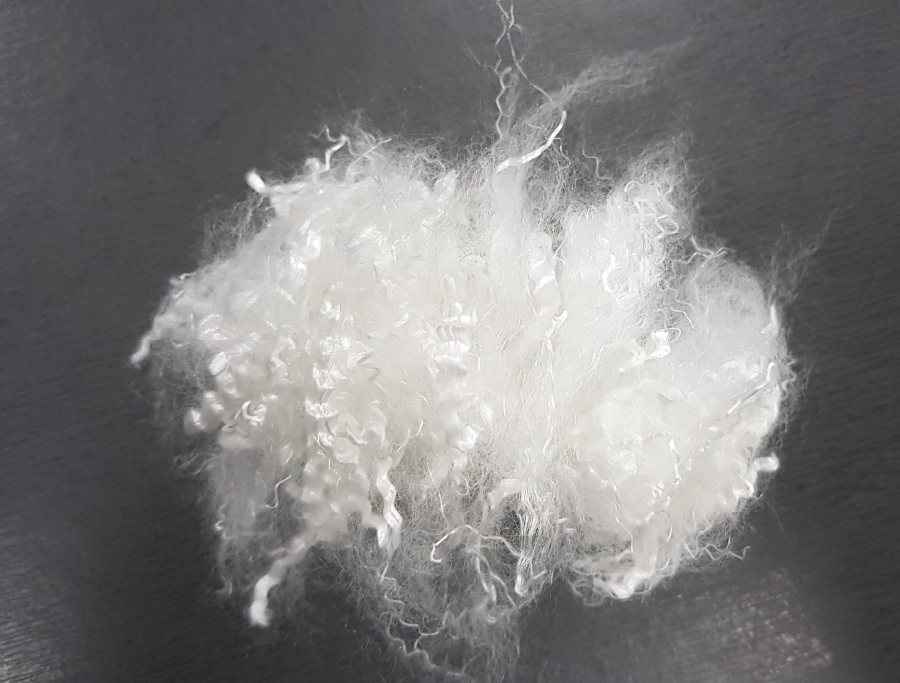
Polyester fibers are dehydrated with dryers to remove the moisure or chemicals lefts and cut short at a certain length to become staple fibers. In general, the cutting length is in between 22 and 102mm. Short fibers and long fibers are manufactured into the form of cotton-like loose fill and sheet-type fill materials, respectively.
If the fiber length is too short, they can have a low bulkiness and are less likely to regain the original shape due to a lack of crimps. If the length is too long, on the contrary, they can be crumpled or folded when they are filled into finished goods. Hence, their length should be determined from the raw materials production stage by considering the types and characteristics to be used, and the know-how and experience of an insulation material provider serves as a critical element that greatly affects the product quality.
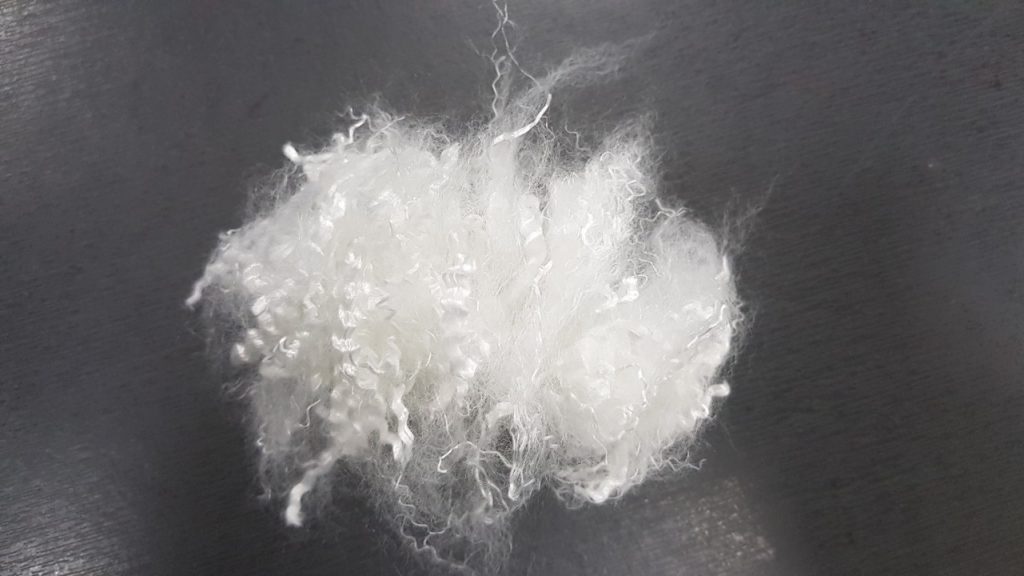

<Image of staple fibers>
5. Packing
After the process, staple fibers are compressed and packed to have a certain weight. A bale of fibers weighs between 250 and 320kg on average, although it differs depending on the bulkiness.

<Fibers after packing>
The characteristics of insulation materials are mostly determined in the raw material stage. Hence, the producer needs to be particularly carefully in the order and quality management of raw materials to fully utilize the characteristics of insulation material. Based on the experience spanning over 2 decades, SynCloud is closely cooperating with quality raw material providers to ensure that the materials can be processed to be used for insulation materials accordingly.
By Park Kyung-jun, SynCloud Part