Synthetic Insulation 101
2020-03-02
There are growing demands for thermal insulation materials, which are associated with down price fluctuations, climate change, and needs for alternatives to animal materials. In response thereto, Pan-Pacific recently decided to merge its natural down insulation brand PRAUDEN and synthetic insulation brand ABSOLON to form the Insulation Business Headquarters with the aim to boost the company’s expertise and efficiency in the insulation business, thereby providing customers with professional consulting services and competitive product offerings. It also aims to combine the best of the two divisions’ experience and skills to develop new products and proactively respond to society’s call on sustainability.
In this newsletter and ones to follow, you will find details about synthetic insulation, the ABSOLON brand that is a maker and supplier of synthetic insulation, and its product offerings. In this article, the focus is on the basic of synthetic insulation.
What is synthetic insulation?
Fibers are natural, or synthetic. Man-made fibers, unlike their natural counterparts, are made from manufacturing process. Among them, synthetic fibers are ones made from petroleum or coal using chemical reactions, and synthetic insulation refers to thermal insulating materials made from synthetic fibers. They are also known as chemical fiber insulation as they are made from chemical reactions.
To sum up, man-made insulation encompasses synthetic insulation, and most of synthetic insulation materials are made from polyester. The most commonly used term “synthetic insulation” is used throughout this article.
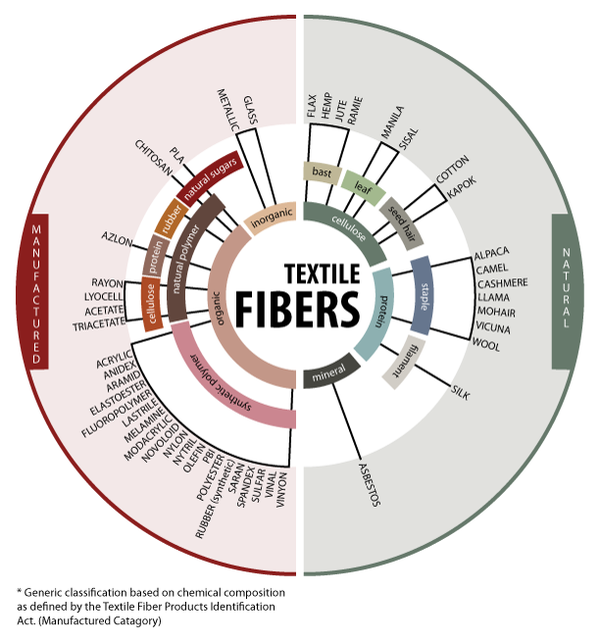
<Classification of textile fibers>
Image Source: T for Textile
Most of synthetic insulation materials are made from polyester, inter alia, polyethylene terephthalate, commonly known as PET. These fibers are manufactured from synthetic polymers that contain at least 85% divalent alcohols (HOROH) and terephthalate ester (ρ-HOOCC 6H 4COOH). They then are processed to make insulation materials in various thickness and length.
Types of synthetic insulation
Synthetic insulation materials are classified into padding or faux down depending on the shapes.

<Padding (left) and faux down (right)>
Padding sheets are easily applicable quilted items. Even thickness and fixed forms ensure great workability.
Faux down is for voluminous items. Its changeable form makes it ideal to be filled in certain parts of clothes.
Benefits of synthetic insulation
Whereas the supply of natural down is limited, the supply of synthetic insulation is more stable thanks to the low variability of raw materials. Being five times cheaper than natural down, it also offers cost competitiveness. Synthetic insulation materials are not absorbent, hence suitable for items involved in vigorous activities. They also make alternatives to animal-derived materials.
Application of synthetic insulation
Synthetic insulation is applicable to various textile products that need thermo-keeping properties. It is used in fashion/outdoor/sportwear, protective suits, beddings, sleeping bags, shoes, and gloves in multifaceted ways. These manufactured materials offer greater potential for development in terms of shapes, compositions, and functions, hence wider applications envisaged.
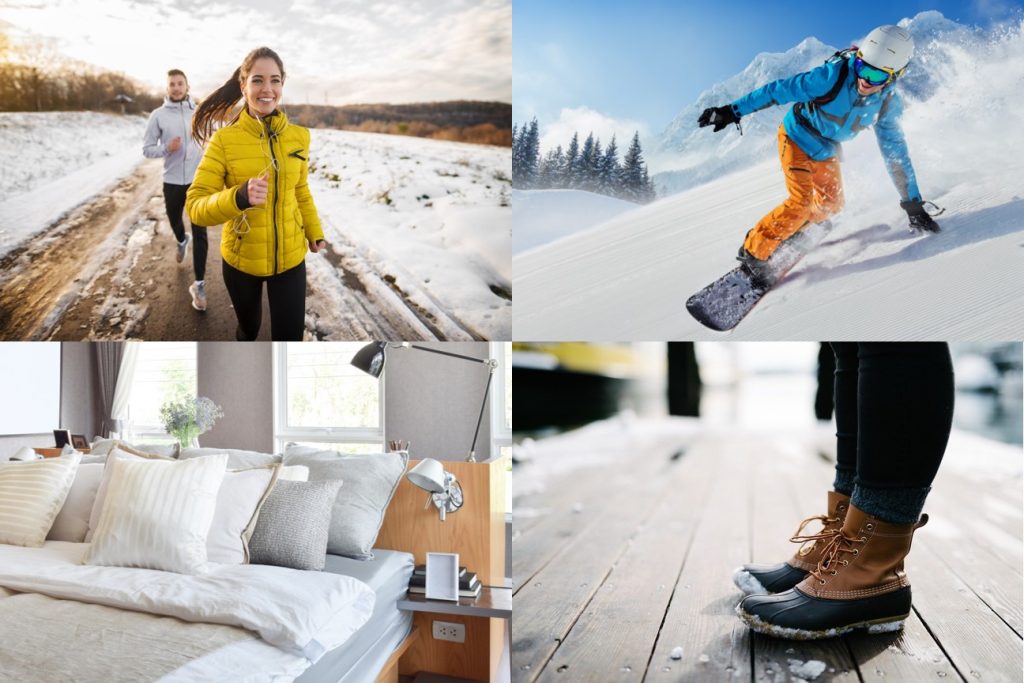 <Examples of the use of synthetic insulation>
<Examples of the use of synthetic insulation>
ABSOLON is a synthetic insulation brand by Pan-Pacific, supplying a range of products with different characteristics and forms to leading local and international brands. These include RCS-certified recycled polyester insulation, biomaterial-based environmentally friendly insulation, and exothermic insulation with graphene.
By Park Kyung-jun, ABSOLON Part